What are the common intestine infections and what causes them? What are the symptoms do you expect? Get information on the various infections including bacterial (including the various bacterial), viral and parasites that commonly affect the intestines. It is not just a list but their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Understanding intestines
Before we look at the various intestinal infections, let us briefly discuss what comprises of intestines and their basic roles. The intestine is part of the lower alimentary canal which begins after the end of the stomach i.e. at the pyloric sphincter and goes all the way to the anus. The intestine is divided into the small intestine that comprises duodenum, jejunum and ileum while the large intestine is “subdivided into the cecum, colon, rectum and the anal canal” [en.wikipedia.org].
The main role of the intestine is food digestion, absorption of nutrients and water to the bloodstream, preparation and storage of feces until defecation or elimination through the anal canal.
Symptoms and signs

When you have an intestinal infection, expect the symptoms to be different. In general, the common symptoms one may have includes the following:
- diarrhea
- fever
- bleeding
- bloating
- abdominal pain
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- vomiting
- weight loss
- dehydration
- mucus or blood in the stool
However, since they are caused by a number of viruses, bacteria, and parasites, it is not reasonable to come up with a list of symptoms since each infection might have slightly different symptoms.
While looking at each of the causes, we will briefly mention the most common specific lower bowel infection symptoms. This will you in identifying the probable cause. We will consider the following gastrointestinal infections:
- Bacterial
- Viral
- Parasitic infections
Bacterial infections – symptoms and treatments
There are many types of intestinal bacterial infections with some of the sharing of some symptoms while others might have slightly different signs and symptoms. While discussing each of the bacteria that cause infections in the intestines, we will also mention something on not only the specific intestinal bacteria symptoms you expect but also treatments if required.
It is worthwhile noting that whereas some might be a small intestine bacterial infection, others affect the large intestine and rectum, we are going to consider general infections that affect the intestine i.e. both large, small and up to the rectum. So, what are the common ones caused by bacteria?
Salmonella infection
This refers to a group of gram-negative bacteria that include Salmonella Enterica, Salmonella Typi, Salmonella paratyphi A, Salmonella schottmuelleri, Salmonella hirschfeldii among other salmonella bacteria variety.
Salmonella is a foodborne often in raw poultry, seafood, beef, eggs, unwashed vegetable and fruits. You can also get them from touching your reptile pets such as turtles, lizards and snakes.
Salmonella symptoms
The common symptoms of this intestinal infection that develop within 8 to 72 hours and last for between 4-7 days include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Blood in stool
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Headache
- Possible nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite
Source: MedlinePlus and Mayo Clinic
Whereas most people get well without treatment, infants (and children), the elderly, and people with other chronic problems including HIV/AIDS, sickle cell diseases, and those taking cancer-fighting medication might seriously be affected and require treatment. Furthermore, if salmonella gets into your bloodstream it can be very serious. Finally, some variety of salmonella often results to typhoid fever which can be very serious and common in developing nations.
Salmonella treatment and cures
For intestinal infection, give fluids by mouth and if severe intravenously. For patients at risk of bacteremias like the old and those with infections such as HIV, use antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin or azithromycin. And if one has bacteremia, ciprofloxacin or ceftriaxone is administered intravenously for two weeks and up to 4-6 weeks if the bacteria persists. Finally, abscesses will require draining and the use of antibiotics for not less than 4 weeks.
Shigella Bacteria gastrointestinal infections
Going on with our discussion on bacterial Intestinal infections, the second common culprit is shigella bacteria. It is a highly contagious infection i.e. intestinal bacterial infection contagious that commonly affects children aged 2-4 years although it can affect anyone. It spreads by coming in contact with contaminated stool, food and drinking water.
Symptoms of shigella bacteria
It is characterized by diarrhea that is bloody (red stool), fever, abdominal cramps and pains as well as fever since it inflames the small intestine lining. Feeling nauseated, and vomiting can also be experienced.
Shigella treatment
While “a mild case usually clears up on its own within a week. When treatment is needed, doctors generally prescribe antibiotics” [mayoclinic.org]. According to medicinenet.com, antibiotics commonly used include ampicillin ceftriaxone (Rocephin), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim or Septra), or ciprofloxacin. Avoid antidiarrheal agents since they can worsen the problem.
Clostridium difficile (c. diff) is another possible bacterial one
This is a bacterial infection that affects the digestive system and affects people who have had antibiotic treatments i.e. it can be caused by antibiotics. It often has mild to severe symptoms which include fever, abdominal cramps that are painful, diarrhea, nausea, and loss of appetite,
It is transmitted by stool from infected people and the bacteria can survive on objects or surface for many weeks or months. If you touch a contaminated surface and touch your mouth or nose, the bacteria can be ingested causing the problem.
Treatment of c. diff
Treatment is mainly by withdrawing from antibiotics that cause the infection, severe cases require the use of vancomycin and metronidazole antibiotics where symptoms start improving after 2-3 and clears up within 7-10 days. Relapse can often occur and further treatment required. Do not ignore it since it can damage the affected part of your bowel requiring removal surgery.
E. coli bacteria
Escherichia coli (E. coli) refers to a variety of bacteria that are found in the intestines of healthy animals and in humans. Although most of them are harmless, there are a few which are harmful i.e. “many types of E. coli, and most of them are harmless. But some can cause bloody diarrhea. Some strains of E. coli bacteria (such as a strain called O157:H7) may also cause severe anemia or kidney failure, which can lead to death” [webmd.com].
- coli is transmitted by coming in contact with the animal and human stool or drinking water or eating food that is contaminated by feces. Raw dairy products, vegetables, fruits and undercooked processed meat can also cause this problem.
According to MedlinePlus, the common symptoms of having E. coli infection include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Severe abdominal cramps
- Watery or very bloody diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Fever
- coli recovers on its own without treatment. Adults with E. coli O157:H7 recover within 7 days (recovery time) without treatment while older people and young children have a risk factor of developing hemolytic uremic syndrome, a type of life threatening kidney failure.
Treatment is by taking water sips to avoid dehydration and at home self-care i.e. at home or natural treatments. Avoid antidiarrheal medications and antibiotics since they will worsen the infection since they slow down digestion giving more time for absorption on toxins (poison) that E. coli produces.
Campylobacter enteritis
This is a relatively common small intestine infection caused by Campylobacter jejuni bacteria which is one the bacteria strains that cause food poisoning or traveler\’s diarrhea. Often, “babies younger than 1 year old, teens, and young adults are most commonly affected” [kidshealth.org].
Normally, Campylobacter is found in domestic and wild animals’ intestines. They are passed out through feces where it can contaminate water and food thus finding its way into our intestines where it attacks intestine lining. It can also cause illness on other body parts especially in a very young kind when it gets into their blood system (bacteremia) and it can rarely cause Guillain-Barre syndrome and autoimmune condition that is very rare.
The common symptoms of intestinal infection due to campylobacter include painful abdominal cramping, fever, vomiting and nausea, and watery diarrhea that might be bloody at times. These symptoms appear between 1 and 7 days of ingestion.
In most cases, affected people can recover without treatment. However, at times, a doctor may recommend antibiotics when symptoms are severe where Azithromycin and fluoroquinolones are commonly used i.e. the common antibiotics for intestinal bacterial infection caused by campylobacter
Intestinal staph – staph food poisoning
Another possible intestinal infection is Staphylococcal food poisoning which is caused by toxins produced by the Staphylococcus aureus bacterium. The toxins can only be transmitted by food and an infected person cannot transmit them to another person.
Foods commonly associated with staph food poisoning include meats, salads including eggs, tuna, chicken, potato as well as macaroni, sandwich fillings, mild, dairy products, eggs and poultry products and meats.
Symptoms of staph food poisoning include retching, vomiting, nausea, abdominal cramping and diarrhea. In some causes dehydration, muscle cramping, headache, changes in pulse rate and blood pressure may occur.
Staph food poisoning resolves within two days but it can take 3 or more days, manage dehydration with rehydration drinks like Pedialyte and avoid any medications unless recommended by a doctor i.e. “do not use medicines, including antibiotics and other treatments unless your doctor recommends them” [webmd.com]. This is often to people with compromised immunity and other underlying diseases.
Listeriosis or listeria
This refers to a very serious infection caused by ingesting food that is contaminated by Listeria monocytogenes bacterium that can survive refrigeration. This infection “primarily affects older adults, pregnant women, newborns, and adults with weakened immune systems” [cdc.gov].
Listeriosis is transmitted through unpasteurized milk, smoked salmon, pre-packed sandwiches, butter, raw vegetables, infected animal meats and process foods like hotdogs, soft cheeks and deli meats.
Symptoms due to Listeriosis
Some of the common intestinal infections symptoms due to listeria infection include fever, diarrhea, muscle aches and nausea that can start showing after a few days but it can take up to two months for the symptoms to show up. Symptoms in newborns and in babies include irritability, fever, vomiting and little or no interest in feeding
If the infection spreads to your nervous system, headache, stiff neck, balance loss, convulsions and confusion and a change in the level of your alertness might change.
Whereas pregnant mothers might be mild to mother, it might cause devastating effects including death before birth and a life-threatening infection in the first few days after birth.
Mild cases might require you to drink lots of fluids and having painkillers to reduce muscle pain and fever. Treatment is by antibiotics where ampicillin is the first choice of medication and gentamicin might be added given intravenously.
Fibrosis (vibrio illness non-cholera)
This infection is caused by Vibrio vulnificus which are gram-negative bacteria that are road shaped that occur in marine and estuarine environments. They can be transmitted to your intestine when you eat undercooked shellfish especially oysters and contaminated water.
On its symptoms, “vibriosis is characterized by diarrhea, primary septicemia, wound infections, or other extraintestinal infections“[cdc.gov]. The diarrhea is non-bloody while some people might vomiting and have abdominal pain.
The sickness often lasts for between 2 to 8 days and “in persons with liver disease, cancer, or another immune-compromising condition, V. vulnificus typically infects the bloodstream, causing a life-threatening illness” [foodsafety.gov]. Death can occur within two days.
Cholera from Vibrio cholerae
According to Wikipedia, “cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium Vibrio cholerae” which can have mild or severe symptoms. It is transmitted by contaminated food and water i.e. contaminated with poop of an infected person. It is common in places with poor sanitation, water treatment and poor hygiene.
When you have it, some of the common symptoms of cholera include watery diarrhea that is severe, stomach cramps, leg cramps, being or feeling sick among others and they occur within a few days after infection. However, they can also begin showing a few hours after one is infected. Excessive vomiting together with diarrhea can cause dehydration and one can go to shock when blood pressure drops massively.
Treatment is by the use of oral rehydration solution and if the diarrhea is severe, antibiotics might be recommended.
Yersiniosis
This is an infectious disease that is caused by a bacterium that belongs to the genus Yersinia with most illnesses caused by Yersinia enterocolitica. This bacterium is transmitted via eating contaminated food, especially or and/or undercooked pork products.
In children, common symptoms will include diarrhea that is often bloody, fever and abdominal pain. The “Symptoms typically develop 4 to 7 days after exposure and may last 1 to 3 weeks or longer. In older children and adults, right-sided abdominal pain and fever may be the predominant symptoms and may be confused with appendicitis” [cdc.gov].
To treat this bacterial intestinal infection, go for antibiotics such as aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolone, doxycycline, or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole if you have a complicated infection while less complicated case will resolve by itself.
Bacillus cereus
This is a bacteria that produces toxins that can cause either diarrhea (diarrheal) or vomiting and nausea (emetic). The bacteria is found in a number of foods that include soups, sauces, leftovers, rice or any food that has been left at room temperature for a long time.
When toxins cause emetic, you will be nausea and vomit and they set in after 30mins to six hours. On the other hand, diarrheal will begin showing signs within 6-15hours after infection and will be characterized by abdominal cramps and watery diarrhea.
The illness will last for a day. Rest and drinking plenty of fluids is often recommended to help treat the condition.
Intestinal viruses or viral gastroenteritis
This refers to the stomach and intestinal inflammation caused by a viral infection. The problem affects people who eat food contaminated with one of the intestinal viruses that cause this problem. We will look at not only how they spread but also intestinal virus symptoms and treatment.
How they’re spread or how do they go around?
Stomach flu or viral gastroenteritis is highly contagious and they spread through eating or drinking contaminated food and water. Furthermore, one can get them by sharing towels, utensils and food with people who are already infected will cause intestinal viruses going around from one person to another. Ensure you prevent stomach flu by avoiding contaminated water and food. Also, people who eat shellfish, undercooked oysters,
Young children, older adults, churchgoers, school children, dormitory residents or people with weakened immunity due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, etc.
Names of intestinal viruses or types of intestinal viruses
Common viruses responsible for in viral gastroenteritis include the following:
Noroviruses
Affects both children and adults and they are the most common cause of food-related diseases in the world.
Rotaviruses
Rotavirus is a common cause of viral gastroenteritis in children where it shows severe symptoms. In adults, it might not have severe symptoms though adults can spread it.
Other viruses are Astrovirus, Enteric adenovirus.
Symptoms of intestinal virus
What are some of the common gastroenteritis infection symptoms? According to Mayo Clinic, “Viral gastroenteritis is an intestinal infection marked by watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea or vomiting, and sometimes fever.” Sometimes, gastroenteritis can “cause severe diarrhea in both adults and children” [nlm.nih.gov], abdominal pain, occasional head and muscle ache. Diarrhea should not be bloody since a bloody one indicates you have a different more severe infection.
Other possible symptoms include weight loss, loss of appetite, sweating and chills. Since most of the lower intestinal virus symptoms, especially diarrhea are also exhibited by various bacterial infections including clostridium difficile, E. coli, salmonella or even parasites like giardia, proper diagnosis is important.
In general, whereas adults may manage may have a fever and manageable intestinal infection symptoms children and babies might have worse symptoms.
How Long Does a Stomach Virus Last?
On how long they last in children and adults or the duration that these stomach viruses last, Mayo Clinic notes that “viral gastroenteritis symptoms may appear within one to three days after you\’re infected and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms usually last just a day or two, but occasionally they may persist as long as 10 days.”
For those whose question is if they can last for weeks, I guess you have the answer from the above with or without treatment.
Diagnosis
A rapid stool test can be used to detect only the norovirus and rotavirus while for other viruses that cause this problem there is not a quick test. This means doctors have to rule out the bacterial and parasitic cause and conclude it could be those viruses.
Intestinal viruses treatment
Being caused by viruses, there is no effective treatment. Any medication would work on reducing the side effects and not cure the virus. CDC advises patients to use OTC oral rehydration solutions, OHS.
Avoid antibiotics since they do not treat illnesses caused by viruses and overuse might cause bacteria strains that are resistant to those antibiotics. Avoid some medications like Aspirin i.e. “Never give aspirin to children or teenagers with a viral illness. This can cause Reye’s syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition” [healthline.com]
Self-care will include having plenty of rest and avoiding some foods such as dairy products, alcohol, caffeine, highly seasoned and fatty foods and nicotine. Furthermore, avoid solid foods for hours to give your stomach a chance to settle, suck ice chips or take small water sips and eat easy to digest foods including toast, soda crackers, banana, rice, gelatin and chicken.
Finally, ensure your kids get rotavirus vaccines.
When to see a doctor

For intestinal viruses in children and infants, see a doctor if fever goes beyond 102F, the child becomes irritable or has a lot of pain and discomfort, has bloody diarrhea and is dehydrated by observing their drinking and urinating rate compared to normal one.
Furthermore, see a doctor if a child’s vomiting does not stop after several hours, doesn’t wet their diapers within a period of about 6 hours, has a sunken fontanel, is drowsy, unresponsive or sleep, has blood stool or diarrhea that is severe, sunken eyes or cries without any tears and/or with a dry mouth.
Adults should see a doctor when you are not able to retain fluids for 24 hours, you have been vomiting for over two days, your vomit has blood, blood during a bowel movement, your fever goes beyond 104 F (40 C) or you are dehydrated. Dehydration can be noted with excessive thirst, little or no urine that is yellow, dry mouth, dizziness, severe weakness, lightheadedness among other symptoms.
Intestinal parasites and worms
Besides the bacterial and viral intestinal infections, one could have parasites as well as worm. The common parasites include the following:
Giardia
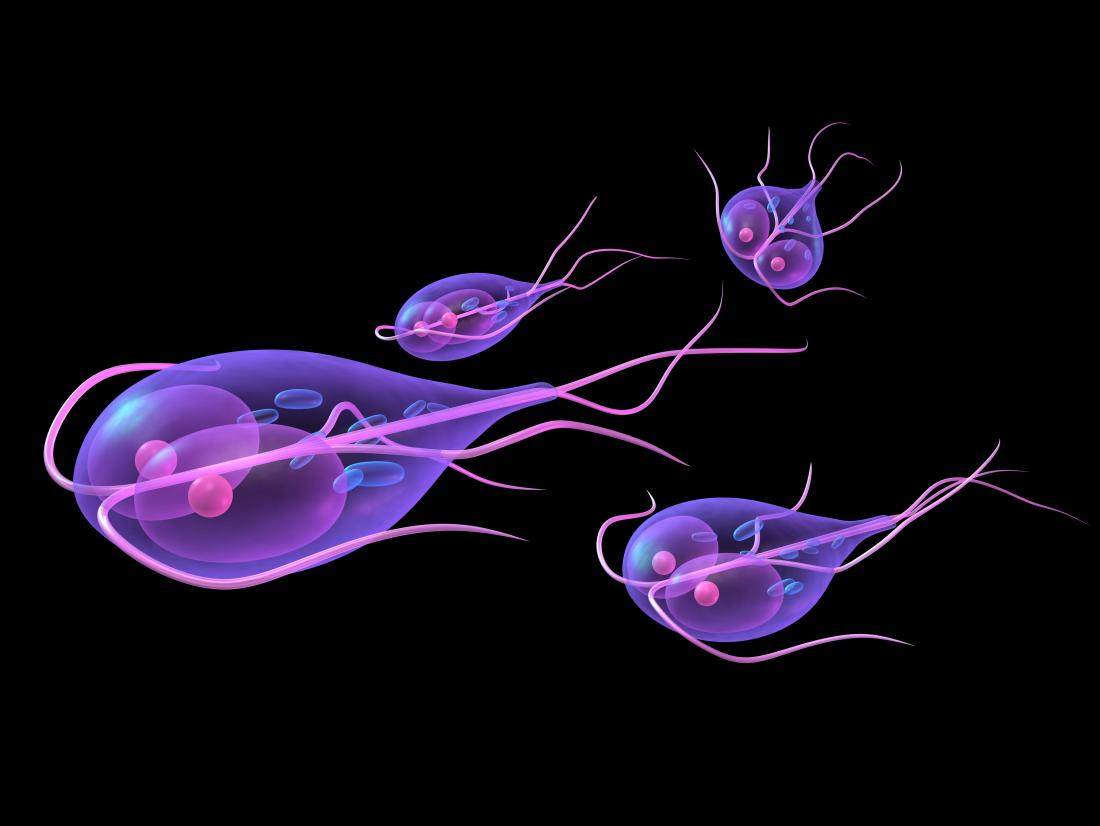
Giardia also is known as Giardia intestinalis, Giardia duodenalis or Giardia lamblia is an intestinal parasite found in soil and water that has been contaminated by the feces of an infected person or animal. It is the protozoan responsible of giardiasis. You can get this illness by drinking water or eating undercooked food with giardia organisms as well as having contact with people suffering from this disease.
According to CDC, common symptoms include diarrhea, gas, stomach pain/cramps, stomach upsets (vomiting and nausea), dehydration and greasy stool which floats.
A number of medications including metronidazole, nitazoxanide and tinidazole can be used. Alternatively, use medications such as aromomycin, furazolidone and quinacrine.
Cryptosporidiosis
This is a diarrheal disease caused by cryptosporidium. There are a number of cryptosporidium species that affect animals and human beings and are commonly spread via recreational and drinking water though they can also be spread by other foods.
Since these protozoan parasites have a hard outer shell, they can tolerate chlorinated water for long periods of time and even stay outside a body for a long time.
Common symptoms you will have include watery diarrhea, dehydration, nausea, fever, vomiting, weight loss, and stomach pain or crams. These symptoms last typically for 1-2 weeks or sometimes up to 4 weeks for people with healthy immune systems.
For people with weak or compromised immunities such as those with HIV/AIDS, transplant and cancer patients, and those with inherited diseases that affect ones immunity might end up with serious or fatal illness.
Healthy people will recover without treatment. They need to take a lot of fluids to avoid dehydration which is more common in pregnant mothers and children. Although anti-diarrheal medications such as Nitazoxanide which is FDA approve can be used, consult a doctor first. HIV patients with this parasite should see their health care provider.
Intestinal yeast overgrowth
Candida overgrowth in intestines (fungal intestinal overgrowth) or intestinal fungi. Common intestinal yeast infection symptoms include diarrhea, intestinal cramps, itching at the anal region, bloating, and constipation among others.
Intestinal worms
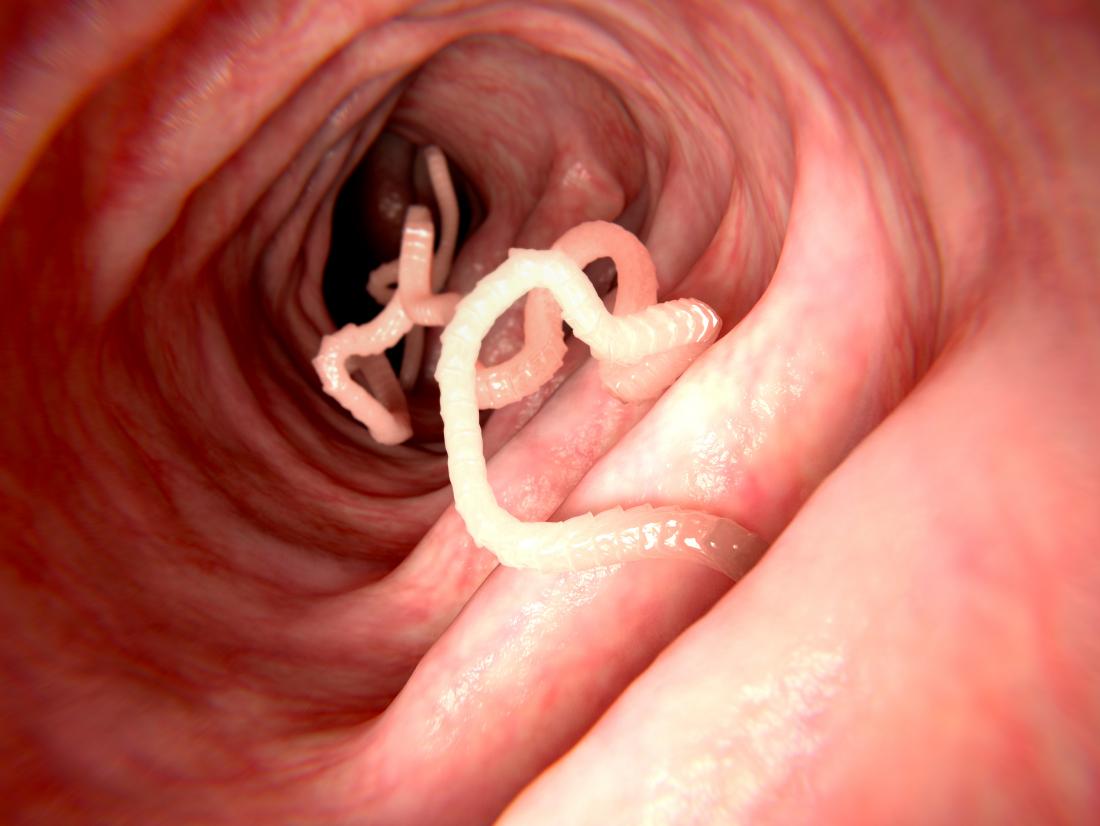
Besides the above infection, another possible cause of some of the symptoms mentioned above is worms. There are many types of worms that include hookworm, tapeworm, pin worm, strongyloides stercoralis, and echinococcosis among others. We intend to cover more on these worms separately.
Other Intestinal diseases that possible cause of intestinal infection like symptoms
Other possible conditions that can affect the intestine include most of which are conditions include the following
- Diverticulitis – This refers to inflammation of diverticula (pouches that form on wall of colon). The condition is characterized by pain on the lower left part of the abdomen, nausea, fever and chills, bloating and gas, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea as well as abdominal tenderness.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease – an autoimmune disease characterized according to Medical University of South Carolina by persistent abdominal pain, bowel sores, diarrhea, weight loss and intestinal bleeding i.e. it causes intestinal bleeding.
- Cancers including rectal, colon, carcinoid tumor, colon polyps and small intestine cancers.
- Intestine obstruction
- Ulcerative colitis
- Colon bleeding
- Cohn’s disease
Note: Diarrhea with shoulder pain, especially right shoulder pain is likely to be pancreas or gallbladder problems.
We were not discussing stomach infections (viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi) but it is worthwhile noting that some of the above intestinal bacterial and viral infections can also be responsible for the various stomach and bowel infections.